 You've spent hours building your Next.js application, deployed it to Vercel, and everything seems perfect—until you start getting reports of mysterious 405 Method Not Allowed errors. Suddenly your API routes are failing, and users can't interact with your application correctly. Even more frustrating, everything works perfectly in your local development environment!
You've spent hours building your Next.js application, deployed it to Vercel, and everything seems perfect—until you start getting reports of mysterious 405 Method Not Allowed errors. Suddenly your API routes are failing, and users can't interact with your application correctly. Even more frustrating, everything works perfectly in your local development environment!
If you're experiencing this exact scenario, you're not alone. 405 errors on Next.js applications deployed to Vercel are common but fixable issues that often stem from subtle configuration mistakes.
What Exactly Is a 405 Error?
A 405 Method Not Allowed error occurs when the HTTP method used in the request is not supported by the server for the requested resource. In simpler terms, you're trying to use an HTTP method (like POST, GET, PUT, or DELETE) that the server doesn't allow for that particular endpoint.
In your browser, it might look something like this:
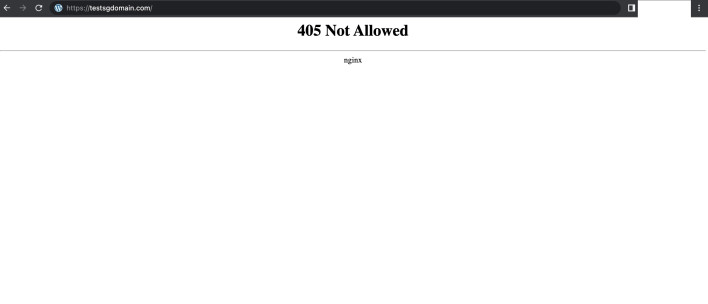 This is especially frustrating because these errors often only appear in production environments like Vercel, while everything works perfectly in local development.
This is especially frustrating because these errors often only appear in production environments like Vercel, while everything works perfectly in local development.
Common Causes of 405 Errors in Next.js Applications
Before we dive into solutions, let's understand the most frequent culprits behind 405 errors when deploying Next.js applications to Vercel:
1. Incorrect API Route Structure
One of the most common issues occurs when developers mix routing patterns between Next.js App Router (app/api/) and Pages Router (pages/api/). Vercel won't recognize your API methods if you're structuring them incorrectly.
As one developer noted in a Reddit discussion:
"If you're using Next.js App Router (app/api/) but defining routes like Pages Router (pages/api/), Vercel won't recognize your API methods."
2. Static Exports Disabling API Routes
If you're using next export or have output: "export" in your Next.js configuration, your API routes will be completely removed during the build process. This happens because static exports can't include server-side functionality like API routes.
3. Missing Environment Variables in Production
Your API might work perfectly locally but fail in production because the required process.env variables aren't configured in your Vercel environment.
4. Middleware Interference
Custom middleware or Vercel Authentication settings can inadvertently block access to your API routes, especially for unauthorized users.
5. Environment Differences
Local development environments often differ from Vercel's serverless runtime in terms of Node.js versions or package dependencies, leading to unexpected behavior.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix 405 Errors
Now that we understand the common causes, let's walk through practical solutions to fix 405 errors in your Next.js application on Vercel:
1. Verify Your API Route Structure
The most critical step is ensuring your API routes follow the correct structure for your chosen routing system:
For App Router (Next.js 13+):
Your API routes should be in
app/api/<route>/route.ts(or .js)You must export the HTTP method functions directly:
// Correct implementation in app/api/example/route.ts
export async function POST(request: Request) {
const data = await request.json();
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ success: true }), { status: 200 });
}
export async function GET() {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ message: "Hello World" }), { status: 200 });
}
For Pages Router (Traditional):
Your API routes should be in
pages/api/<route>.ts(or .js)Export a default function that handles different methods:
// Correct implementation in pages/api/example.ts
import type { NextApiRequest, NextApiResponse } from 'next';
export default function handler(req: NextApiRequest, res: NextApiResponse) {
if (req.method === 'POST') {
// Handle POST request
res.status(200).json({ success: true });
} else if (req.method === 'GET') {
// Handle GET request
res.status(200).json({ message: "Hello World" });
} else {
// Handle any other HTTP method
res.setHeader('Allow', ['GET', 'POST']);
res.status(405).end(`Method ${req.method} Not Allowed`);
}
}
2. Avoid Static Exports for Applications with API Routes
If you're using API routes, you cannot use static exports. Check your package.json and next.config.js files for:
// In package.json - Remove or comment this line
"build": "next build && next export"
// In next.config.js - Remove or modify this configuration
module.exports = {
output: 'export' // Remove this line if using API routes
}
3. Configure Environment Variables in Vercel
To ensure your production environment has access to all necessary variables:
Go to your project in the Vercel dashboard
Navigate to Settings > Environment Variables
Add all required environment variables that your application needs
Redeploy your application after adding variables
Remember that environment variables in local development (e.g., in your .env.local file) are not automatically transferred to Vercel.
4. Adjust Middleware to Allow API Access
If you're using custom middleware, make sure it's not blocking your API routes:
// In middleware.ts
import { NextResponse } from 'next/server';
import type { NextRequest } from 'next/server';
export function middleware(request: NextRequest) {
// Allow API routes to pass through without interference
if (request.nextUrl.pathname.startsWith('/api')) {
return NextResponse.next();
}
// Your other middleware logic here
// ...
}
5. Match Local and Production Environments
Ensure your Node.js version and dependencies match between local and production environments:
Specify the Node.js version in your package.json:
"engines": {
"node": "18.x"
}
Lock your dependency versions to prevent unexpected updates:
npm ci # Instead of npm install when setting up the project
Use Vercel's local development tools to simulate the production environment:
npm install -g vercel
vercel dev
Advanced Debugging for Persistent 405 Errors
If you've followed the steps above but are still encountering 405 errors, you'll need to dive deeper into debugging:
Inspect Vercel Deployment Logs
Vercel provides detailed logs that can help identify the root cause:
Go to your project in the Vercel dashboard
Navigate to the Deployments tab
Click on the deployment having issues
Select "Functions" to see logs related to your API routes
 These logs often reveal issues like missing modules, runtime errors, or incorrect configurations that aren't apparent in local development.
These logs often reveal issues like missing modules, runtime errors, or incorrect configurations that aren't apparent in local development.
Test API Endpoints Directly
Use tools like cURL or Postman to test your API endpoints directly, which can provide more detailed error information:
curl -X POST https://your-app.vercel.app/api/your-endpoint -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"key": "value"}'
This approach helps isolate whether the issue is with your API implementation or with how your front-end is calling the API.
Force Dynamic Rendering
In some cases, Next.js might be caching your API responses or using static generation inappropriately. You can force dynamic rendering:
// In app/api/example/route.ts
export const dynamic = 'force-dynamic';
export async function POST(request: Request) {
// Your code here
}
Check for CORS Issues
Sometimes what appears as a 405 error might actually be related to CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) policies:
// In next.config.js
module.exports = {
async headers() {
return [
{
source: '/api/:path*',
headers: [
{ key: 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', value: 'true' },
{ key: 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin', value: '*' },
{ key: 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods', value: 'GET,DELETE,PATCH,POST,PUT' },
{ key: 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers', value: 'X-CSRF-Token, X-Requested-With, Accept, Accept-Version, Content-Length, Content-MD5, Content-Type, Date, X-Api-Version' },
],
},
];
},
};
Preventative Measures
To avoid 405 errors in future deployments, implement these best practices:
1. Use a Staging Environment
Before pushing to production, deploy to a staging environment that mirrors your production setup. This catches environment-specific issues early.
vercel --env production
2. Implement Proper Error Handling
Add comprehensive error handling to your API routes:
export async function POST(request: Request) {
try {
const data = await request.json();
// Process data
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ success: true }), { status: 200 });
} catch (error) {
console.error('API error:', error);
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ error: 'Internal Server Error' }), {
status: 500,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }
});
}
}
3. Set Up Monitoring
Use Vercel Analytics or a third-party monitoring tool to get alerts about API failures in real-time.
Conclusion
The 405 Method Not Allowed error in Next.js applications on Vercel typically results from mismatches between development and production environments, incorrect API route structures, or middleware interference. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide, you can identify and fix these issues.
Remember that the key to preventing these errors lies in understanding the differences between Next.js routing systems, avoiding static exports for applications with API functionality, and ensuring consistent environments across development and production.
For more information on handling errors in Next.js, refer to the official Next.js documentation on error handling, and for Vercel-specific deployment issues, check out Vercel's troubleshooting guide.
By implementing the preventative measures suggested above, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering 405 errors in the future and ensure a smoother experience for both you as a developer and your users.


